What is Zirconia? - From minerals to high-tech materials
Zirconia (chemical formula ZrO₂) is a white inorganic compound that mainly exists in the form of oblique zircon and zircon in nature. Its crystal structure is complex. It is a monoclinic crystal system at room temperature and can be transformed into a square or cubic crystal system at high temperature. This phase transition characteristic makes it both a challenge and an opportunity in industrial applications.
Key Features:
Ultra-high melting point (2680℃) and boiling point (4300℃), excellent fire resistance;
Hardness is second only to diamond (Mohs hardness 7.5), wear resistance is extremely strong;
Chemical inertness: acid and alkali resistance, corrosion resistance, excellent biocompatibility;
Photocatalytic activity: can decompose pollutants, used in environmental protection field.
2. The “cross-border” application of zirconia-an all-around player from medical care to aerospace
Medical field: the "invisible guardian” of teeth and bones
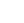
Dental restoration: Zirconia porcelain teeth have become the mainstream choice due to their high light transmittance, no metal odor and biocompatibility. For example, DMAX Demei porcelain zirconia all-ceramic teeth can make long bridge restorations of more than 6 units.
Artificial joints: Zirconia ceramics have strong wear resistance and no barrier to X-rays. Patients do not need to remove them for imaging examination after surgery.
Industrial manufacturing: the ultimate solution for high temperature and high pressure
Refractory material: Zirconia crucible can withstand a high temperature of 2700℃ and is used for smelting precious metals and aerospace materials;
Ceramic knives: Zirconia knives have high hardness, corrosion resistance, and no metal ion release, making them a food-grade safety tool.;
Sensor: In the catalyst carrier of automobile exhaust gas, zirconia helps convert carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides to improve environmental protection efficiency.
Electronics and Energy: the “Driving Force behind Future Technology”
Fuel cell: Zirconia is used as an electrolyte material to accelerate the conduction of hydrogen and oxygen ions and improve energy conversion efficiency;

Oxygen sensor: accurately detects the oxygen content of molten metal, which is used in steel smelting and industrial waste gas treatment.
3. Preparation of zirconia: precision technology from ore to nano powder
Traditional craftsmanship:
Chlorination method: Using zircon as raw material, high-purity zirconia is prepared by chlorination, oxidation and other steps;
Sulfuric acid method: low cost but limited purity, commonly used in industrial grade products.
Advanced technology:
Sol-gel method: Preparation of nanoscale zirconia with uniform particle size and good dispersion, suitable for biomedical materials;
Hydrothermal method: High crystallinity zirconia is generated at high temperature and pressure, which is used in precision ceramic coatings.
4. Product case analysis-How does zirconia change lives?
Argen HT+ML high permeability zirconia crown:
45% transparency + 1250MPa strength, simulates the gradient layer of natural tooth enamel, and can show a natural luster after glazing, without the need for complex dyeing processes.
Zirconia ceramic bearings:
High temperature resistance, oil-free and self-lubricating, used in aviation engines and precision instruments, the life span is 3 times higher than that of metal bearings.
Zirconia-based thermal barrier coating:
It is used in turbine engine blades to reduce the operating temperature by more than 200℃ and extend the service life of equipment.
5. The future of zirconia: the Integration of Green Technology and smart materials
Environmental protection field: Photocatalytic zirconia coating can decompose air pollutants and be used for self-cleaning of urban buildings;
Smart wearable: nano zirconia flexible sensor, real-time monitoring of human health data;

3D printing: High-precision zirconia powder promotes the development of customized medical implants, such as personalized artificial joints.
Conclusion: Zirconia-Small Materials Leverage Large Industries
From dental clinics to spaceports, zirconia quietly penetrates the core of modern technology with its “hard-core” properties. With the innovation of preparation technology (such as the breakthrough in nano-coating of domestic Chongqing Jifeng Technology), this material is opening up unlimited possibilities from industry to consumer fields with lower cost and higher performance. In the future, zirconia may become the key driver of the transition from the “carbon age” to the “ceramic age”.





 Home
Home Product Center
Product Center Telephone
Telephone Message
Message